Duty and delta are often used parameters during the computation of crop water requirements of a commanded area. Delta indicates the water requirement for a crop and duty indicates the efficiency of water in the irrigation canal .
Delta of a crop:
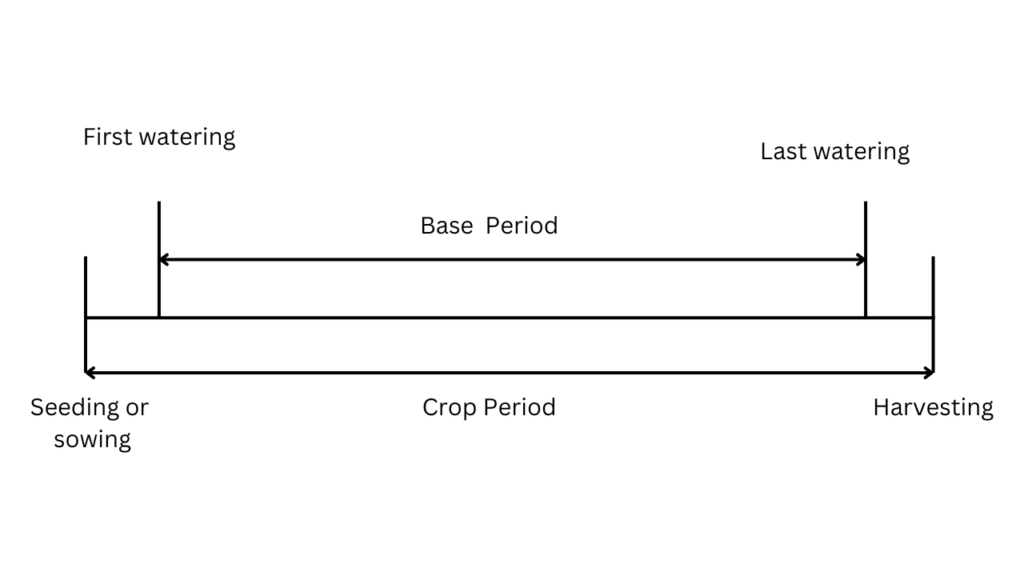
A certain amount of water is required for the healthy growth of each crop for its maturity. If the total amount of water supplied to a crop from it’s first watering to last watering is stored on impervious land , then there will be a certain depth of water above the land which is commonly known as delta for this crop and it is denoted by symbol (Δ). So, delta of a crop is defined as the total depth of water supplied to a crop from its first watering to its last watering. Delta might be different for different types of crop. Generally delta (Δ) is measured in centimeter (cm).
Below is an example for calculation of delta of a crop.
If a crop requires about 6 cm of water after every 16 days, and the base period for this crop is 128 days. Find the Delta (Δ) for this crop.
Here,
Number of watering = 128/16 =8
Total depth of water required in base period = 8*6 cm = 48 cm
Hence Δ for this crop = 48 cm
Duty
The number of hectares that can be irrigated by constant supply of water at the rate of one cumec throughout the base period is known as duty. Duty is measured in hectare/cumecs. The duty of water is not a fixed quantity, it varies with different factors like nature of soil, method of ploughing etc.
For Example,
A land of 5 ha area is being irrigated by a continuous supply of water at the rate of 2 cumecs. Find the duty of the water.
Here,
2 cumecs of water irrigates 5 hectare of land.
So, 1 cumec of water irrigates 5/2 = 2.5 hectares of land.
Thus, duty = 2.5 hectare/cumecs.
Base Period
Base period is the time period between the first watering of a crop to it’s last watering just before the maturity of crop. Base period is measured in terms of number of days.
Crop Period
Crop period of a crop is defined as total time that elapse between sowing of crop and it’s harvesting . So, crop period can be also defined as the total time period for which the crop remains in the field. Crop period is also measured in days.
so, Crop period > Base period for all type of crops.
Relation between Duty and Delta
Suppose ∆ be the delta of a crop in m which is the total depth of water required for the growth of crop on the field during it’s entire base period (B days). Let ‘D’ be the duty of water in the field in hectare/cumecs (ha/(m3/s)) .
Consider, 1 cumecs of water is applied for this crop on field for B days continuously. Then, total volume of water applied to this crop during B days =V = 1 m3/s * B days (=24*60*60 sec)
V=86400B m3
According to the definition of duty(D) , 1cumecs of water supplied for B days matures D hectare of land. So , the quantity of water ‘V’ obtained above matures ‘D’ hectare of land.
1 hectare=10,000 m2 or 104 m2.
Now, the depth of water applied on this land = Volume/Area
=(86400B)/(D *10000) m
=8.64 B/D
This is equal to delta of crop (‘∆’).
∆=8.64B/D
This is the required relationship between duty and delta(∆) where delta is in m , base period (B) is in days and Duty (D) is in hectare/cumec.
Example :
Find the ∆ for sugarcane when its duty is 500 ha/cumec on the land and base period is 106 days .
Solution,
We have,
∆=8.64B/D
∆=8.64*106/500
∆=1.831m = 183.17 cm
Thus the delta for this sugarcane on the specified field is 183.17 cm .
